How Can The Carbon Stored In Plants Reach The Atmosphere?
Biologic carbon dioxide can come from decomposing organic matter forest fires and other land use changes. Capturing and storing that excess carbon by boosting the capacity of natures own carbon-storing technology plants.
What Is The Carbon Cycle What Is The Science Behind It United States Carbon Cycle Science Program Source: www.carboncyclescience.us
It is one method of reducing the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere with the goal of reducing global climate change.
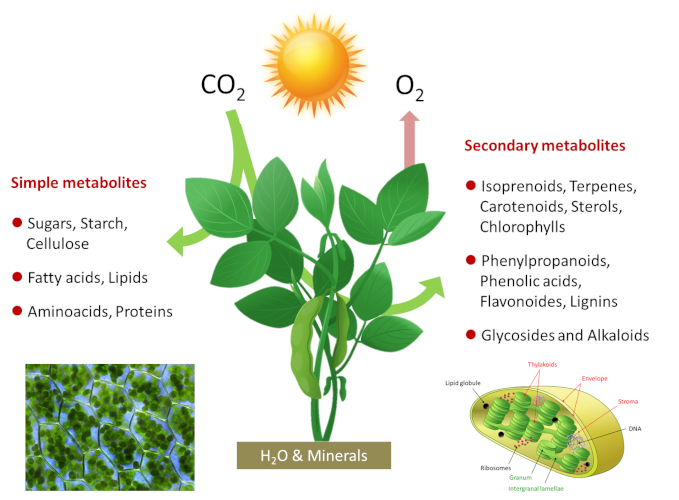
How can the carbon stored in plants reach the atmosphere?. Carbon sequestration is the process of capturing and storing atmospheric carbon dioxide. What the plant doesnt need for growth is exuded through the roots to feed soil organisms whereby the carbon is humified or rendered stable. For example some carbon in the atmosphere might be captured by plants to make food during photosynthesis.
All of these land use decisions are helping plants absorb human-released carbon in the Northern Hemisphere. In North America CO 2 is the main greenhouse gas GHG emitted into the atmosphere accounting for 79 percent of Canadas total GHGs. As autotrophs add or subtract carbon dioxide from the water through photosynthesis or respiration they modify this balance allowing the water to absorb more carbon dioxide or causing it to emit carbon dioxide into the atmosphere.
And after plants die they decay releasing the carbon to the atmosphere. Its a range of technologies that either. December 1 - 31 2010 PNG.
It is estimated that carbon capture and storage technologies can capture more than 90 percent of CO 2 emissions from power plants and industrial facilities. Carbon stored in plants reaches the atmosphere via cellular respiration. Plants also need water sunlight and nutrients especially nitrogen.
This carbon can then be ingested and stored in animals that eat the plants. The build-up of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases in the atmosphere can trap heat and contribute to climate change. What carbon dioxide they dont use they exhale releasing the leftover gas with oxygen.
Some of this sediment might form fossil fuels such. Scientists have found that a. As plants photosynthesize they absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere.
Soils potential to soak up planet-warning carbon dioxide has been overestimated by as much as 40 say scientists. Its a demand-side approach to reducing the threat of climate change and lately its been gaining some extra research steam. In many places we prevent plant carbon from entering the atmosphere by extinguishing wildfires.
Usually the CO 2 is captured from large point sources such as a chemical plant or biomass power plant and then stored in an underground geological formation. What is carbon capture. The USGS is conducting assessments on two major types of carbon.
Direct air capture which pulls CO2 from the atmosphere rather than just catching pollution at a source like a power plant and can be combined with underground storage. Through photosynthesis a plant draws carbon out of the air to form carbon compounds. The energy from the glucose molecules is broken down into ATP.
Man-made carbon dioxide can come from burning coal natural gas and oil to produce energy. Stop carbon dioxide from entering the atmosphere often by filtering out the carbon dioxide en route to the smokestack of a. Some of that carbon makes its way into the soil and some of that soil.
They take carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and turn it into the sugars that become leaves stems roots and woody trunks. This allows woody material which stores carbon to build up. 2 before it enters the atmosphere transporting it and storing it for centuries or millennia.
When the animals die they decompose and their remains become sediment trapping the stored carbon in layers that eventually turn into rock or minerals. The planets plants pull CO 2 out of the atmosphere and store it in their leaves stems and roots. In a typical growing season plants can pull as much as 100 gigatons of carbon from the atmosphere as they photosynthesizeUnder normal circumstances much of this is eventually released back into.
When plants die the carbon goes into the soil and microbes can release the carbon back into the atmosphere through decomposition. There is a limit to how much carbon plants can take out of the atmosphere and that limit varies from region to region. Carbon dioxide is the most commonly produced greenhouse gas.
If a plant doesnt have one of these things it wont grow regardless of how abundant the other necessities are. Forests are typically carbon sinks places that absorb more carbon than they release. Cellular respiration is the set of metabolic reactions that allows plants to convert the energy from nutrients into ATP adenosine triphosphate and then release the waste products.
The aim is to prevent the release of CO.
Cycle Of Carbon Nitrogen Oxygen And Hydrogen Carbon Cycle Nitrogen Cycle Earth Science Source: www.pinterest.com
The Path Of Carbon In Photosynthesis Encyclopedia Of The Environment Source: www.encyclopedie-environnement.org
Carbon Cycle And Atmospheric Co2 Earth 530 The Critical Zone Source: www.e-education.psu.edu
Learn About Fossil Fuels Science For Kids Carbon Cycle Nitrogen Cycle Science For Kids Source: www.pinterest.com
Https Www Esrl Noaa Gov Gmd Education Info Activities Pdfs Tbi Co2 And The Carbon Cycle Pdf Source:
Lab 2 The Carbon Cycle What Goes Around Comes Around Carbon Cycle Ap Environmental Science Environmental Science Source: www.pinterest.com


